About lithium battery charging principles and specifications
- Three-stage charging principle of lithium battery:
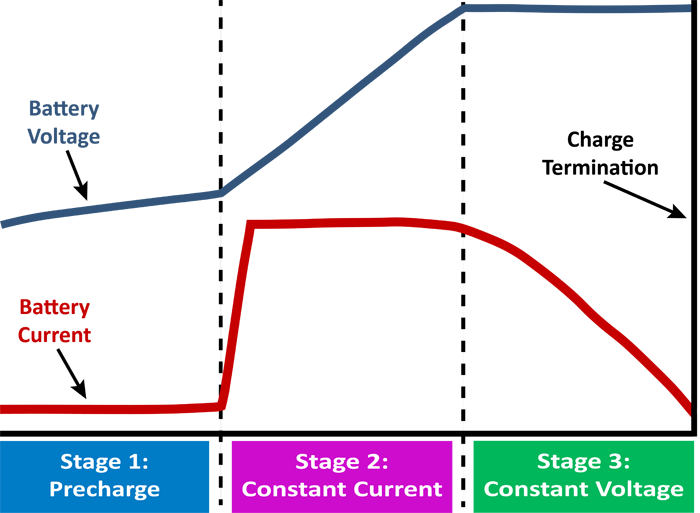
Phase 1: Trickle Charge
Trickle charge is used to pre-charge (recovery charge) a fully discharged battery cell. When the battery voltage is lower than about 3V, trickle charging is used, and the trickle charging current is one-tenth of the constant current charging current, that is, 0.1c (take the constant charging current as 1A for example, the trickle charging current is 100mA)
Phase 2: Constant current charging
When the battery voltage rises above the trickle charging threshold, the charging current is increased for constant current charging. The constant current charging current is between 0.2C and 1.0C. The battery voltage gradually increases with the constant current charging process. Generally, the voltage set by a single battery is 3.0-4.2V.
Phase 3: Constant voltage charging
When the battery voltage rises to 4.2V, the constant current charging ends and the constant voltage charging phase begins. The current is based on the saturation of the battery cell. As the charging process continues, the charging current gradually decreases from the maximum value. When it decreases to 0.01C, the charging is considered to be terminated. (C is a method of comparing the nominal capacity of the battery with the current. For example, if the battery has a capacity of 1000mAh, 1C is the charging current of 1000mA.)
- Specifications for fast charging of lithium batteries:
The BC1.2 specification also determines how each port should enumerate to the end device and a protocol that identifies the type of application port.
The three USB BC1.2 port types are SDP, DCP, and CDP.
Three ports of BC1.2
* Standard downstream port (SDP)
This port has 15kΩ pull-down resistors on the D + and D- lines. The current limit value is discussed above: 2.5mA when suspended, 100mA when connected, and 500mA when connected and configured for a higher power.
* Dedicated charging port (DCP)
This port does not support any data transmission but can provide more than 1.5A. There is a short between the D + and D- lines of the port. This type of port supports higher charging wall chargers and car chargers.
* Charging downstream port (CDP)
This port supports both high-current charging and full USB 2.0 data transfer. The port has the 15kΩ pull-down resistor necessary for D + and D- communication, and it also has an internal circuit that switches during the charger detection phase. Internal circuitry allows portable devices to distinguish CDP from other types of ports.
